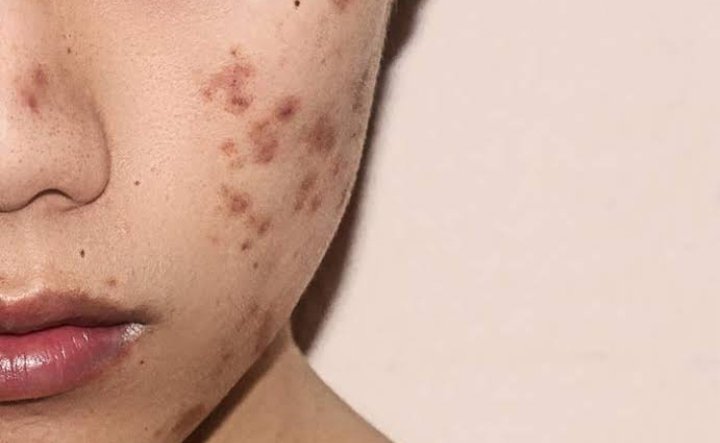
What is Hyperpigmentation?.

Hyperpigmentation is the word used to describe areas of uneven pigmentation in the skin. It often appears as dark patches or spots that make your skin look uneven. These spots are known as age, liver or sun spots and can appear on any part of the body that is regularly exposed to the sun.
Hyperpigmentation is also at the heart of skin conditions such as Melasma and Post-inflammatory hyperpigmentation.
MELASMA .
Melasma, characterised by larger patches of hyperpigmentation, is most common in women and is often triggered by changes in hormone levels.
POST-INFLAMMATORY HYPERPIGMENTATION.
This condition is often found among acne sufferers and occurs when a skin injury heals and leaves an area of discoloration behind.
If you’re dealing with hyperpigmentation, know that you aren’t alone.
Hyperpigmentation is a common skin condition, and there are a number of different treatment options available.
What can I do to treat Hyperpigmentation?.
1. Night Cream.
If you’re suffering from any kind of pigmentation, it’s really important to use products with ingredients that can help brighten the skin and to use them regularly. Building a routine and sticking to it is key.
As part of that routine, we highly recommend the use of Night Cream. It has been clinically tested & proven to significantly reduce the appearance of age spots in just 2 weeks. Not only that, but it also works to prevent their reappearance.
Night Cream works in harmony with your skin to help enhance, protect and nourish the skin. With continued use, it is capable of evening skin tone, reducing the appearance of imperfections, and protecting against environmental damage.
2. Face acids.
Face acids, or skin acids, work by exfoliating, or shedding, the top layer of your skin.
Whenever you exfoliate your skin, new skin cells emerge to take the place of the old ones. The process helps even out your skin tone and makes it smoother overall.
Many face acids are available OTC at beauty stores and drugstores. Popular options include: Kojic acid, salicylic acid e.t.c.
Who should try this?
Face acids work well for mild hyperpigmentation on fairer skin tones.
3. Retinoids.
Derived from vitamin A, retinoids are among some of the oldest OTC skin care ingredients used. Their small molecular structure allows them to penetrate deep into the skin and treat the layers below your epidermis.
Retinoids can come in either a prescription or OTC formula. However, OTC versions tend to be weaker. If you don’t see any results after a couple of months, talk with your dermatologist about the prescription retinoid tretinoin(Retin-A).
Who should try this?
OTC retinoids may be safe for all skin tones, but you should double-check with your dermatologist if you have darker skin and plan on using these products long term.
It’s also important to note that retinoids are more often used to treat wrinkles than hyperpigmentation. This means that retinoids may not be the best first line treatment.
4. Chemical peel.
A chemical peel uses acids at stronger concentrations to treat the desired area of skin. They reduce the appearance of hyperpigmentation by removing the top layer of your skin epidermis). Deeper versions may also penetrate the middle layer of your skin (dermis) to produce more dramatic results.
Although many chemical peels are available you might consider getting a professional-grade peel at your dermatologist’s office. These are more powerful, and they yield quicker results.
Due to their strength, in-office peels may also increase your risk for side effects. Talk with your dermatologist about your individual risks.
Possible risks with both at-home and in-office chemical peels;
- redness
- irritation
- blistering
- infection
- scarring
- allergic reaction
If you’re out in the sun on a regular basis, chemical peels may not be the best treatment option for you. Chemical peels cause your skin to be more sensitive to the sun’s rays.
If you don’t adequately apply sunscreen and use other UV protection, the sun may worsen your hyperpigmentation. You’ll need to take extra precautions for at least one week after your last chemical peel.
Who should try this?
Chemical peels may work best for fairer skin tones, and they may provide faster results than face acid products.
5. Laser peel (skin resurfacing).
A laser peel(resurfacing) treatment uses targeted beams of light to reduce hyperpigmentation.
There are two types of lasers: ablative and non-ablative.
Ablative lasers are the most intense, and they involve removing layers of your skin. Non-ablative procedures, on the other hand, target the dermis to promote collegen growth and tightening effects.
Ablative lasers are stronger, but they may cause more side effects. Both destroy elements in your skin to ensure that new skin cells grow back tighter and more toned.
Who should try this?
There isn’t a one-size-fits-all approach to skin resurfacing.
Ablative lasers may work better for people with fair skin. For some people, non-ablative versions may cause the skin to darken instead of lighten.
Your dermatologist will work with you to assess your discoloration and overall skin tone to select the best option for your skin.
The Best Ways to Prevent Future Hyperpigmentation.
Today, there are plenty of dark-spot correctors to choose from — but it’s just as essential to tackle them preventively. The following scientifically proven steps can help.
1. Keep Skin Moist To Boost Cell Turnover.
While your primary goal with hyperpigmentation is to lighten the dark spots, an effective over-the-counter (OTC) moisturizer should contain ingredients that benefit the skin in other ways. “In addition to addressing the pigment issues, a good product will have moisturizing agents like glycerin or hyaluronic acid, and maybe even a retinol to boost cell turnover,” says Doris J. Day MD, “These inactive ingredients allow the active brighteners to work more effectively.”
A good moisturizer can also restore the skin’s lipid, or fat, barrier, helping new skin cells stay healthy as they rise to the surface in place of old ones.
2. Keep Hands Off Bug Bites, Blackheads, And Other Injuries.
As tempting as it may be to scratch a mosquito biteor squeeze a stubborn blackhead, remember your mother’s warning — “Don’t pick!” — and follow that advice. “Scratching and picking at a spot will only increase the inflammation that’s responsible for skin discoloration,” says, Jeanine Diwnie, MD, a dermatologist and the director of Image Dermatology in Montclair, New Jersey. “The more you mess with it now, the worse it’ll look later”.
3. Explore OTC Whitening Options.
The sooner you treat hyperpigmentation, the easier it will be to erase. “The pigment in brown spots can move deeper into the skin over time,” Dr. Downie explains.
Spot-eradicating ingredients to look for in OTC treatments include azelaic and glycolic acids, Vitamin C, and retinoids, says the Academy of Dermatology Association (AAD).
Treatments containing ingredients like vitamin C, licorice root, and kojic acid help reduce hyperpigmentation by inhibiting tyrosinase, an enzyme responsible for the formation of skin-darkening melanin.
While many of these OTC ingredients have “bleaching” effects on dark spots, the AAD strongly cautions against applying liquid bleach to your skin.
4. Consider An RX For Stubborn Skin Discolorations.
If OTC remedies aren’t helping, it’s time to call in the pros. Dermatologists consider products with hydroquinone, alone or combined with other lighteners, to be the gold standard for fading dark spots because it slows the production of pigment.“It’s our go-to,” says Downie, “because unlike many of the ingredients in OTC products, it almost always works at eliminating hyperpigmentation.” Have your dermatologist closely monitor hydroquinone treatment, she adds, because in high concentrations hydroquinone can cause sun sensitivity and may bleach the skin.
In addition to hydroquinone, the AOCD notes that your dermatologist may prescribe other treatments such as tretinoin, a type of synthetic Vitamin A.